A Practical Guide with Applications
Selecting the correct boiler capacity is arguably the most critical step in engineering any industrial heating system. This decision determines not only the initial capital expenditure but also the ongoing operational efficiency and the reliability of your entire production line. For Electric Boilers, where power consumption directly impacts the electric bill, accurate sizing is paramount.
An undersized electric boiler can lead to pressure drops, production bottlenecks, and costly reliance on standby fuel sources. An oversized one results in unnecessarily high CAPEX and may operate less efficiently due to frequent cycling.
At IndianBoilers.com, we provide a full spectrum of high-efficiency electric heating solutions. To ensure you select the perfect fit, whether it’s the compact ELECTRON – Electric Steam Boiler, the high-pressure ELECTROMAX – Electric IBR Steam Boiler, or the cutting-edge INDUCTRON – Induction Boiler, this guide outlines the practical steps and critical factors in determining the right capacity for your specific application.
1. Understanding Boiler Capacity Metrics
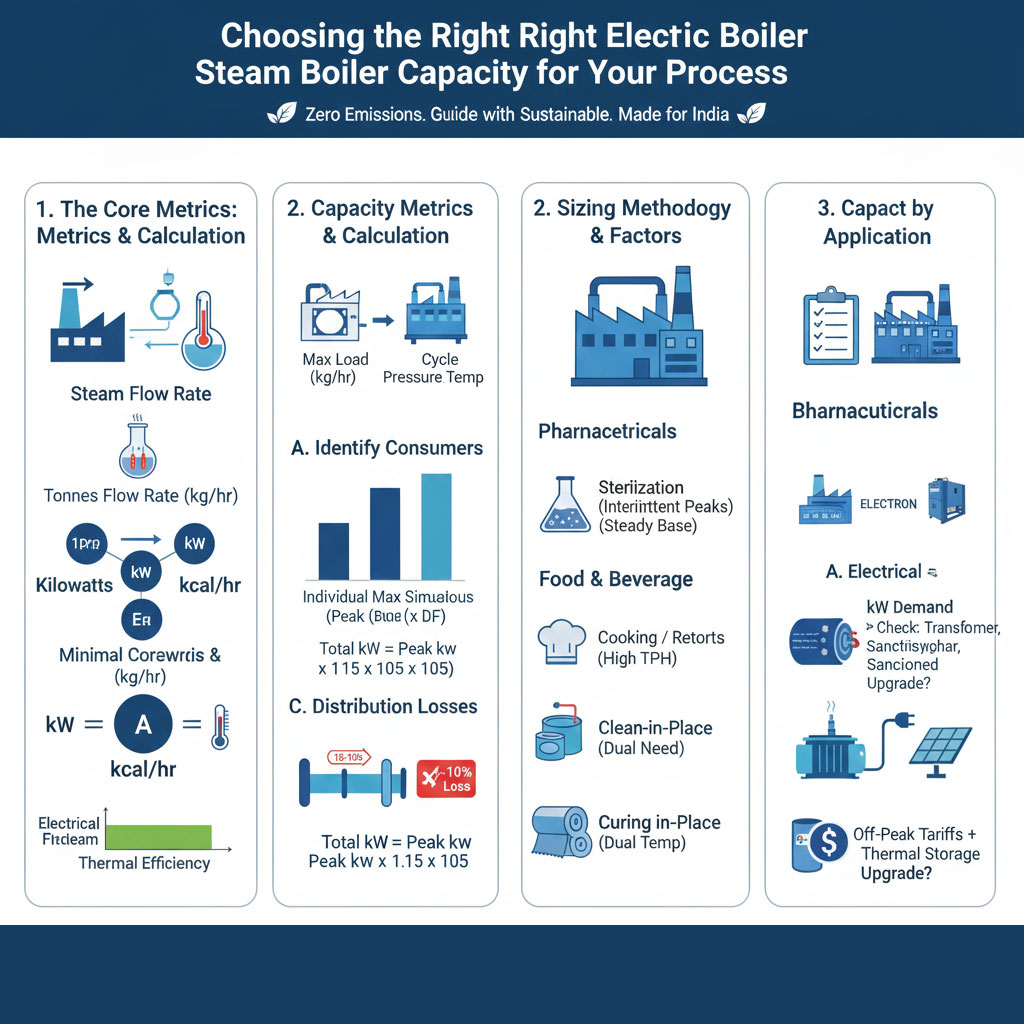
Industrial boiler capacity is measured in three primary units. For electric boilers, capacity is most often expressed in $\text{kW}$ or $\text{Tonne/hr}$.
| Unit | Description | Relationship |
| Tonnes of Steam per Hour (TPH) | The mass flow rate of steam generated. | 1 TPH approx 640 kW (Approximate for saturated steam) |
| Kilowatts (kW) | The electrical power input required. | This is the direct power draw of the electric boiler. |
| Kilocalories per Hour (kcal/hr) | The heat energy output required. | 1 kW approx 860 kcal/hr |
2. Step-by-Step Capacity Calculation Methodology
A precise capacity determination involves a detailed energy audit of all steam consumers in your plant.
A. Identify All Steam/Heat Consumers
List every piece of equipment that requires steam, hot water, or thermal fluid. For each consumer, identify:
- Maximum Load: The maximum instantaneous heat rate required by the machine.
- Operating Cycle: The duration and frequency of the peak load.
- Pressure/Temperature Requirements: The required operating conditions.
B. Calculate Simultaneous Peak Demand (The Diversity Factor)
It is highly unlikely that every single machine will demand its maximum load at the exact same moment. The Diversity Factor (DF) accounts for the staggered operation of equipment.
Diversity Factor: This factor is empirically derived or based on industry averages (typically 0.6 to 0.9).
- Example: In a textile dye house with 10 machines, some are heating up, some are soaking, and some are cooling. If the sum of all peak loads is 5,000 kg/hr, a realistic DF of 0.7 means the simultaneous peak demand is 3,500 kg/hr.
- The Safety Margin: Always add a safety margin of 10% to 15% to the calculated simultaneous peak load to account for:
- Unexpected surges in demand.
- Minor steam leaks in the distribution system.
- Future planned capacity expansion.
C. Account for Distribution Losses
Even with excellent insulation, some heat will be lost from the steam distribution piping, especially in long pipe runs. Add 5% to 10% of the simultaneous peak demand to cover these losses.
3. Capacity Selection by Application
Different industrial sectors exhibit highly specific steam consumption patterns, which directly influence the choice between the ELECTRON, ELECTROMAX, and INDUCTRON series.
A. Pharmaceutical and Healthcare (ELECTRON / INDUCTRON)
| Application | Steam Use Pattern | Key Sizing Factors | Recommended Product |
| Sterilization (Autoclaves) | High, short-duration peaks; intermittent use. | Rapid ramp-up time; steam purity; compact size. | ELECTRON (Small/Medium kW): Ideal for decentralized use near labs/autoclaves, minimizing distribution losses. INDUCTRON (Medium kW): Superior purity and reliability due to non-contact heating. |
| Humidification | Low, steady base load; continuous. | Minimal turndown requirement; precision control. | ELECTRON (Low kW): Perfect for precise, low-volume output for HVAC. |
B. Food and Beverage (ELECTROMAX / INDUCTRON)
| Application | Steam Use Pattern | Key Sizing Factors | Recommended Product |
| Cooking / Retorts | Large, high-pressure steam required for batch cooking; simultaneous large loads. | High TPH capacity; IBR compliance; stable pressure. | ELECTROMAX (High kW / TPH): Required for IBR compliance at higher pressures, ensuring stable operation for continuous production. |
| Clean-in-Place (CIP) | Intermittent high-temperature hot water and low-pressure steam. | High-volume hot water and low-pressure steam flexibility. | ELECTRO AQUA (Hot Water) + ELECTRON (Steam): An efficient combination to meet dual needs. |
C. Textile and Garments (ELECTROMAX / ELECTROPAC)
| Application | Steam Use Pattern | Key Sizing Factors | Recommended Product |
| Dyeing & Finishing | Pulsating load (heating up a dye batch); high total volume. | High TPH capacity; robustness against load swings; precise temperature control. | ELECTROMAX –Electric IBR Steam Boiler (High kW / TPH): Essential for handling the large, cyclical load swings common in dye baths while maintaining IBR-level pressure. |
| Curing / Setting | High-temperature process heat; no pressure required. | High temperature, safety, and precision. | ELECTROPAC – Electric Thermic Fluid Heater: Ideal for processes requiring temperatures up to 300 C without the complexity or high pressure of steam. |
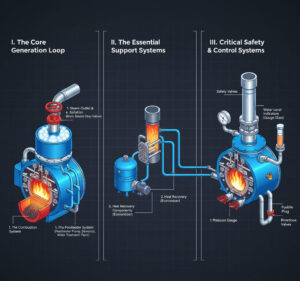
4. Why Electric Boiler Type Matters for Sizing
The choice between the main electric boiler types influences how you think about sizing and system design.
A. Resistance Heating (ELECTRON, ELECTROMAX)
- Sizing Impact: Capacity is directly proportional to the number and size of the immersed heating elements. Sizing is straightforward: match kW Required to the total rated kW of the elements.
- Operational Consideration: As resistance elements are prone to scaling (if water treatment is poor), capacity can degrade over time. Sizing should account for planned maintenance where elements are cleaned or replaced.
B. Induction Heating (INDUCTRON)
- Sizing Impact: Capacity is determined by the size of the induction coil and the flow rate through the heating core.
- Operational Consideration: Because the INDUCTRON is highly scale-resistant on the heating surface, its rated capacity is maintained consistently over time. This high reliability can sometimes allow for slightly tighter sizing compared to resistance systems, provided the safety margin is still maintained for peak demand.
C. Hot Air Generation (ELECTROAIR)
For drying and curing processes, sizing the ELECTROAIR – Electric Hot Air Generator requires calculating the required air flow rate (CFM) and the temperature rise (Delta T).
5. Critical Planning: Electrical Infrastructure and Utility Costs
An accurate capacity calculation is meaningless without confirming the plant’s ability to supply the power and absorb the cost.
A. Assessing Electrical Load
- Large kW Demand: Electric boilers draw massive amounts of power. A 5 TPH ELECTROMAX boiler might require approximately 3,200 kW (or 3.2 MW) of power.
- Infrastructure Check: The calculated kW demand must be confirmed against:
- The capacity of the main incoming transformer.
- The capacity of the plant’s main switchgear and electrical feeders.
- The permissible sanctioned load from the utility company.
If the calculated kW exceeds the sanctioned or infrastructure capacity, the project must factor in the cost and time for an electrical upgrade.
B. Optimizing Operation with Time-of-Use Tariffs
For high kW electric boilers, operating costs are highly sensitive to utility tariffs. The sizing should allow for operational flexibility to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
- Thermal Storage: Oversizing slightly may be strategically beneficial if it allows the boiler to operate exclusively during cheaper, off-peak hours (e.g., at night), storing the steam/heat energy in an accumulator or large pressure vessel for use during the expensive peak hours. This strategy can drastically lower the effective operational cost of the ELECTROMAX or ELECTROPAC system.
Conclusion: Partner with Expertise for Precision Sizing
Choosing the correct capacity for your electric boiler is a high-stakes calculation that balances CAPEX, OPEX, and production reliability. Guesswork leads to guaranteed efficiency losses or production outages.
At IndianBoilers.com, our engineers utilize sophisticated load profiling tools, considering the diversity factors and specific application requirements of your industry—from the batch-wise demands of pharmaceuticals to the continuous loads of large textiles. We ensure the kW capacity of your chosen system—be it the compact ELECTRON, the IBR-compliant ELECTROMAX, the specialized ELECTROPAC, or the innovative INDUCTRON—is perfectly matched to your process.
Don’t compromise on efficiency or reliability. Ensure your electric boiler is sized precisely for peak performance.
Contact IndianBoilers.com today for a detailed, no-obligation steam and heat demand audit tailored for electric system conversion.