Industrial Uses of Steam Boilers & How They Work: Powering the Modern World
Steam boilers are the unsung heroes of modern industry, providing the thermal energy necessary for countless manufacturing processes, sterilization procedures, and power generation. The ability to efficiently convert water into high-energy, transportable steam makes the boiler an indispensable asset in sectors ranging from pharmaceuticals to heavy manufacturing.
Understanding the dual facets of a boiler—its robust mechanical operation and its diverse applications—is key to maximizing plant efficiency and achieving energy goals.
At IndianBoilers.com, we lead the way in providing tailored steam solutions. Our product range encompasses traditional combustion systems and cutting-edge electric technology: the reliable STEAMJET – Oil / Gas Fired Steam Boiler, the sustainable STEAMGEN – Wood / Briquette Fired Steam Boiler, the clean ELECTROMAX – Electric Steam Boiler, and the advanced INDUCTRON – Induction Boiler.
This guide provides a comprehensive look at how steam boilers function and explores their critical roles across various industrial landscapes.
1. How a Steam Boiler Works: The Fundamental Thermodynamic Process
A steam boiler operates by applying heat energy to water within a pressurized system to force a phase change from liquid to gas (steam). This process harnesses the massive amount of latent heat stored in the steam, making it an ideal medium for energy transfer.
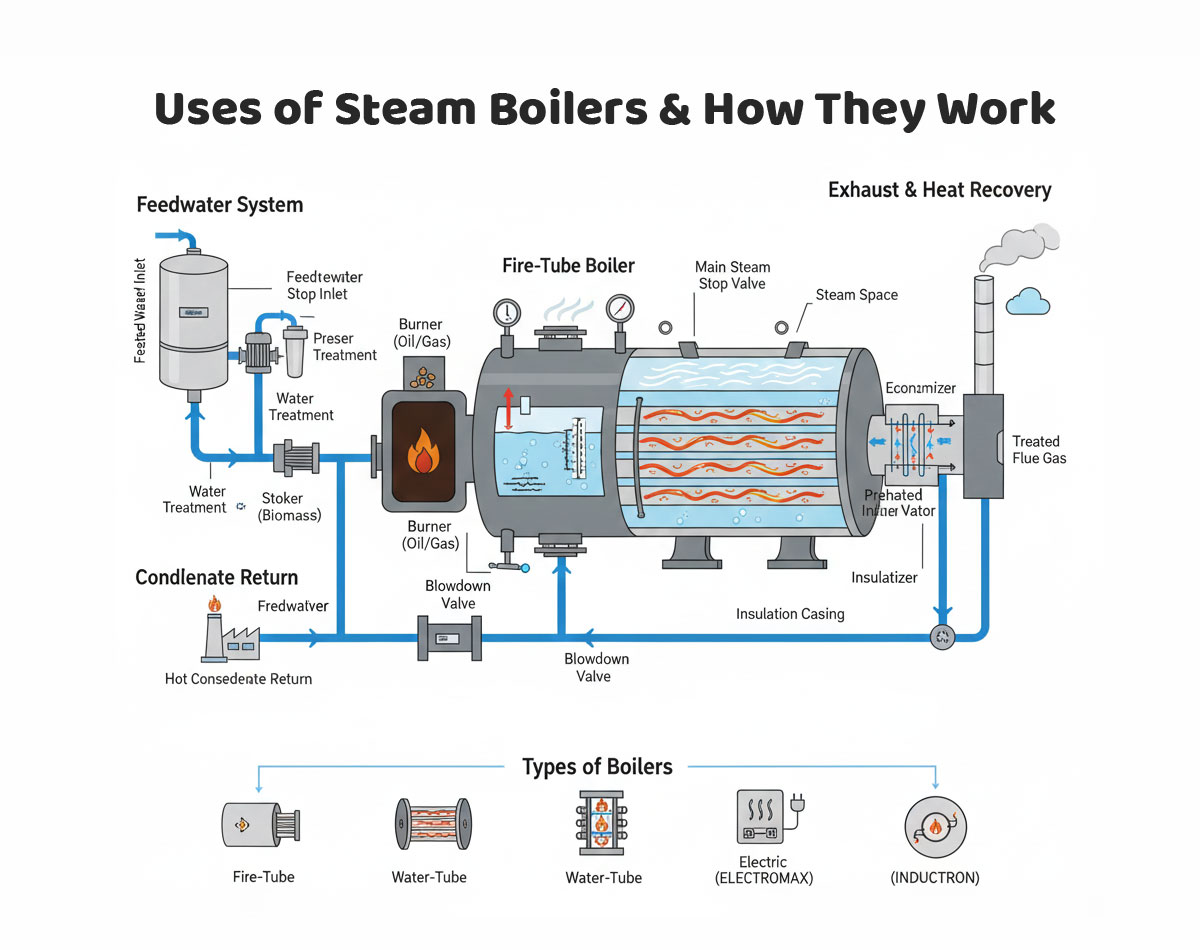
A. The Boiler System Cycle
The operation of all industrial boilers, regardless of fuel, follows a continuous cycle:
- Feedwater Treatment and Supply: Raw water is chemically treated (softened, de-aerated, and conditioned) to remove scale-forming minerals and corrosive dissolved gases O2, CO2). This treated feedwater is then pumped into the boiler vessel.
- Heat Generation:
- Combustion Boilers (STEAMJET, STEAMGEN): Fuel (gas, oil, wood, etc.) is mixed with combustion air and ignited in the furnace. This generates intensely hot flue gases.
- Electric Boilers (ELECTROMAX, INDUCTRON): Electrical energy is converted to heat either through resistance elements or an induction field.
- Heat Transfer: This is the core function. Heat is transferred from the hot gases or heating elements to the water:
- Fire-Tube Boilers: Hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water.
- Water-Tube Boilers: Water flows inside tubes surrounded by hot gases.
- Electric Boilers: Heating element/core is immersed in or adjacent to the water.
- Vaporization: As the water absorbs heat and reaches its boiling point (which increases with pressure), it flashes into saturated steam. The steam collects in the upper section of the boiler (steam drum/space).
- Steam Distribution: The saturated steam is routed to the plant’s distribution header, ready for process use.
- Condensate Return: After releasing its heat energy in the process equipment, the steam condenses back into hot water (condensate). This valuable condensate is collected in a return system and sent back to the feedwater tank, completing the closed loop.
B. Efficiency and Pressure
- Saturated Steam: The steam produced directly from boiling water at a specific pressure. This is used for nearly all process heating (e.g., dyeing, cooking, sterilization) because it releases a large amount of latent heat upon condensation.
- Boiler Efficiency: Modern combustion boilers (like STEAMJET) achieve efficiencies of 80% to 88%. Electric boilers (like ELECTROMAX and INDUCTRON) achieve nearly 99.5% efficiency by eliminating exhaust stack heat losses.
2. Industrial Uses of Steam Boilers: Applications Across Key Sectors
Steam is versatile because it is easily generated, reliably controlled, and provides intense heat transfer, often required by regulations.
A. Power Generation (The Largest Scale Use)
- How it Works: In utility power plants and large captive power generators, high-capacity, high-pressure water-tube boilers (often fueled by STEAMJET or STEAMGEN fuel sources) generate superheated steam.
- Application: This high-energy steam is fed into large turbines, causing the blades to spin. The turbine is connected to a generator, converting the kinetic energy into electricity. Used across thermal power plants (coal, gas, biomass) and Waste-to-Energy plants.
B. Food & Beverage Processing (Safety and Precision)
- Pasteurization: Continuous, precise heating of milk, juices, and other liquids is achieved using steam passed through heat exchangers to ensure microbial safety (HTST process).
- Retort Cooking/Sterilization: High-pressure steam is required in sealed vessels (retorts) to sterilize packaged foods (e.g., canned goods), guaranteeing long shelf life and eliminating pathogens.
- Cooking and Heating: Steam is used in jacketed kettles, ovens, and cookers for mass production of baked goods, confectionery, and prepared foods.
- Sanitation: High-temperature steam and hot water (provided by an ELECTROMAX or ELECTRO AQUA) are vital for Clean-in-Place (CIP) procedures, ensuring piping and tanks are sterile and meet FSSAI standards.
C. Pharmaceutical and Healthcare (Purity and Validation)
- Sterilization:Autoclaves use saturated steam to sterilize surgical instruments, media, and raw materials. This process is highly regulated and must be validated (GxP compliance).
- Electric Preference: ELECTROMAX and INDUCTRON are often preferred here due to their zero on-site emissions, eliminating the risk of combustion byproducts NOx, SOx) contaminating clean rooms or adjacent air intakes.
- Humidification: Clean steam is injected into HVAC systems to maintain precise humidity levels in sterile clean rooms.
- Water Production: Steam is a heat source for Multiple Effect Water Stills used to produce Purified Water (PW) and Water for Injection (WFI).
D. Textiles, Paper, and Manufacturing (High-Volume Heat)
- Textiles: Steam is used extensively for dyeing (heating dye baths), finishing (curing/setting fabrics), and sizing (treating yarn). These processes often involve massive, cyclical steam loads, requiring the high-capacity, IBR-certified power of the STEAMJET or ELECTROMAX.
- Paper & Pulp: High-pressure steam cooks wood chips into pulp and dries the final paper product.
- Rubber Curing: Steam provides the necessary heat and pressure in autoclaves for vulcanizing and curing rubber products (e.g., tires).
E. Specialized High-Temperature Applications
- While steam is capped by pressure, the resistance heating principle is adapted for even higher temperatures using thermal fluid. The ELECTROPAC – Electric Thermic Fluid Heater uses electric heat to circulate synthetic oil up to 350 C for chemical reactors and specialized curing processes where steam pressure would be excessive.
3. The Shift to Electric Boilers: Operational Advantages
While fuel-fired boilers (STEAMJET, STEAMGEN) remain essential for very large capacities and areas with low fuel costs, electric boilers are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for industrial processes due to their unique operational benefits:
| Operational Benefit | Electric Boilers (ELECTROMAX, INDUCTRON) | Fuel-Fired Boilers (STEAMJET, STEAMGEN) |
| Environmental Impact | Zero on-site CO2, NOx, SOx. | High on-site emissions; requires stack and environmental permits. |
| Efficiency | 99.5% (Instant and stable). | 80% – 88% (Losses up the stack). |
| Maintenance | Low: No burner tuning, no refractory repair, no soot blowing. | High: Requires extensive fire-side cleaning and maintenance. |
| Safety | Superior: No combustion, no fuel storage, no fire risk. | Requires strict handling and fire suppression protocols. |
| Control | Excellent: Fast ramp-up and precise modulation (ideal for critical processes). | Good, but slower response due to burner lag. |
| Footprint | Compact: No need for fuel tanks, pumps, or chimneys. | Large footprint required for boiler, auxiliaries, and fuel storage. |
The ELECTROMAX provides the high-capacity, clean solution, while the INDUCTRON ensures scale-resistant, sustained efficiency, making them strategically valuable assets for industries where clean operation and low downtime are paramount.
Conclusion: Steam—The Unstoppable Utility
Steam boilers are the foundation of process heating, providing energy for safety, quality, and production worldwide. The continuous need for efficiency, however, is driving industry toward cleaner solutions.
IndianBoilers.com offers the expertise to guide your plant’s energy strategy. Whether you require the high energy density of the STEAMJET and STEAMGEN systems or the ultimate precision and environmental benefits of the ELECTROMAX and INDUCTRON electric solutions, we ensure your steam generation is efficient, reliable, and perfectly matched to your industrial application.
Ready to optimize your heat process and upgrade your boiler system?
Contact IndianBoilers.com today for an application-specific audit and a detailed analysis of your next steam solution.