The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Electric Steam Boilers: Clean, Efficient, and Future-Proof Heating
For decades, industrial steam generation was synonymous with combustion—burning fossil fuels like coal, diesel, or gas to heat water. While effective, this process brought with it the burdens of air pollution, volatile fuel costs, complex regulatory compliance, and significant maintenance overhead.
Today, the industrial landscape is undergoing a silent but profound transformation: electrification.
The Electric Boiler has emerged as the definitive solution for modern, clean, and efficient process heating. These advanced systems produce high-quality steam with zero on-site emissions, making them the cornerstone of any plant pursuing decarbonization, operational simplification, and superior safety.
At IndianBoilers.com, we lead this charge with a comprehensive portfolio of electric heating solutions. From the precision of the compact ELECTRON – Electric Steam Boiler to the robust, IBR-compliant power of the ELECTROMAX – Electric IBR Steam Boiler, and the next-generation efficiency of the INDUCTRON – Induction Boiler, we provide the ultimate guide to understanding, selecting, and implementing this critical technology.
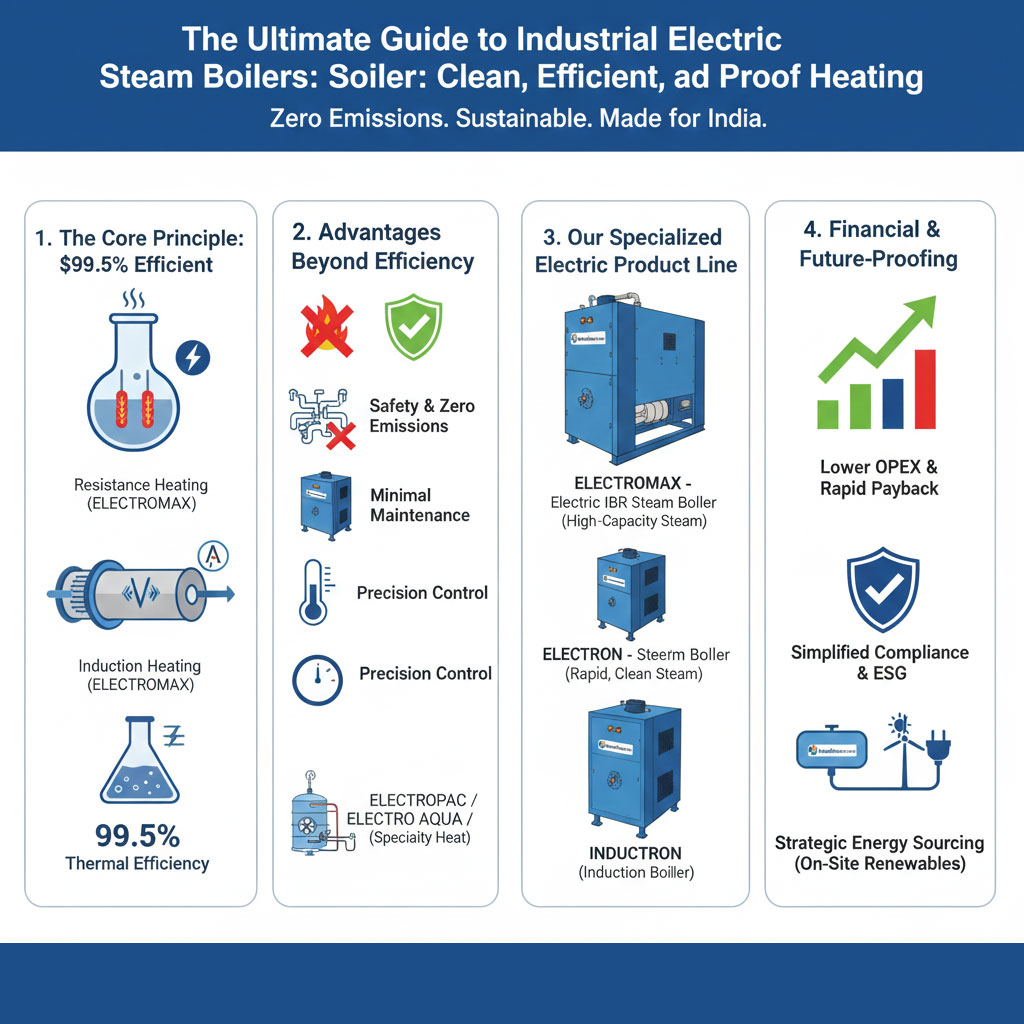
1. The Core Principle: Why Electric Heating is 99.5% Efficient
The fundamental advantage of an electric boiler lies in its heat transfer mechanism. Unlike combustion boilers, which lose up to 25% of potential energy up the stack as hot exhaust gases, electric boilers convert nearly all input electricity into usable thermal energy.
A. The Mechanism: Resistance vs. Induction
Industrial electric boilers primarily use two highly efficient technologies:
i. Resistance Heating (Used in ELECTRON and ELECTROMAX)
- Principle: Electric current flows through immersed heating elements (resistors). The resistance generates heat due to the Joule effect.
- Process: These elements directly transfer heat to the surrounding water, rapidly generating steam or hot water.
- Efficiency: The heat transfer happens directly within the boiler shell, minimizing losses and pushing thermal efficiency close to 99.5%.
ii. Induction Heating (Used in INDUCTRON)
- Principle: An electrical coil induces an alternating electromagnetic field. This field generates eddy currents directly within a special metallic core (the heat exchanger).
- Process: The core heats up instantly, and this heat is then transferred to the water flowing over it. The coil itself is separate from the fluid.
- Advantage: This non-contact method virtually eliminates the primary maintenance headache of resistance boilers: scale buildup on the heating element surfaces.
B. Defining the Efficiency Metric
The efficiency of an electric boiler is defined as:
Since the heat generated is contained within the pressure vessel, losses are negligible, resulting in the near 100% efficiency that makes these systems so appealing despite the higher cost per unit of electrical energy compared to raw fuel.
2. Advantages Beyond Efficiency: Safety, Compliance, and Operation
The benefits of electric boilers extend far beyond thermal efficiency, fundamentally improving the operational environment of any plant.
A. Safety and Maintenance
| Feature | Electric Boiler | Combustion Boiler | Operational Impact |
| Combustion Risk | Zero. No flame, no fuel storage. | High: Fuel leaks, explosion, fire risk. | Superior plant safety and lower insurance premiums. |
| Emissions | Zero on-site CO2, NOx, SOx. | High CO2 and pollutant output. | Eliminate air quality permits and associated compliance costs. |
| Maintenance | Minimal: Periodic inspection of elements/core and standard water-side maintenance. | High: Soot blowing, burner servicing, refractory repair, stack cleaning. | Significantly reduced OPEX and downtime. |
| Noise | Quiet operation. | Loud (burners, fans, combustion noise). | Improved working environment. |
B. Precision Control
Electric power allows for highly granular control over the heating rate. Systems can quickly ramp up and down output by switching heating element stages (in ELECTRON or ELECTROMAX) or modulating the electromagnetic field (in INDUCTRON). This ensures steam quality and pressure are maintained within tight tolerances, crucial for sensitive processes like pharmaceuticals, sterilization, and precision drying.
3. IndianBoilers.com’s Specialized Electric Product Line
We offer specific electric heating solutions tailored to meet the varied demands of modern industries:
A. High-Capacity, IBR-Compliant Steam (ELECTROMAX)
The ELECTROMAX – Electric IBR Steam Boiler is designed for continuous, high-volume steam applications requiring regulatory compliance.
- Target Industry: Large textile units, chemical plants, breweries, and food processing facilities with significant steam demand.
- Key Feature: Built to the highest IBR standards for safety and pressure rating, allowing high-capacity operation without the environmental complexity of a fossil fuel system.
B. Compact, Rapid Steam and Utility (ELECTRON)
The ELECTRON – Electric Steam Boiler serves the need for smaller, instant steam generation where space is limited and startup time must be minimal.
- Target Industry: Laboratories, hospitals (sterilization), small bakeries, and standby steam applications.
- Key Feature: Fast start-up time and compact footprint. Ideal for decentralized steam generation closer to the point of use, minimizing distribution losses.
C. The Next-Generation Solution (INDUCTRON)
The INDUCTRON – Induction Boiler represents the future of electric steam generation. By eliminating direct contact between the heating element and the fluid, it drastically mitigates scaling and corrosion issues on the heat transfer surface.
- Benefit: Maximized element life, reduced water treatment expenses, and sustained $99.5\%$ efficiency over a longer service interval.
D. Specialized Heat Transfer (ELECTROPAC, ELECTRO AQUA, ELECTROAIR)
Not all heat is steam. Our other electric solutions meet specialized needs:
- ELECTROPAC – Electric Thermic Fluid Heater: Provides precise, very high-temperature heat (up to 350 C) without high pressures, essential for specialized chemical and manufacturing processes.
- ELECTRO AQUA – Electric Hot Water Boiler: Efficiently provides low-to-medium temperature hot water for laundries, domestic use, and washing stations.
- ELECTROAIR – Electric Hot Air Generator: Delivers clean, flameless hot air for sensitive drying and curing processes where combustion gases cannot be tolerated.
4. Financial and Strategic Considerations for Investment
While electric boilers have a higher initial capital cost (CAPEX), the long-term financial case is robust due to reduced OPEX and strategic benefits.
A. Operational Cost Savings (OPEX)
- Fuel Handling: Eliminate costs associated with fuel purchase, storage, transportation, and waste disposal.
- Maintenance: The dramatic reduction in maintenance activities (no soot blowing, no burner service) translates directly into thousands saved annually and prevents costly downtime.
- Water Treatment: While necessary, the precision of electric heat can sometimes simplify treatment relative to the challenges posed by combustion.
B. Strategic Energy Sourcing
The true economic viability of an electric boiler hinges on the cost of industrial electricity. Forward-thinking plants employ two strategies:
- Time-of-Day Tariffs: Use the electric boiler during off-peak hours when power rates are lowest. Generating and storing thermal energy in a pressure vessel can optimize energy consumption.
- On-Site Renewables: Pair the electric boiler with a captive solar or wind power plant. This creates a genuine zero-cost, zero-emission heating system, maximizing ROI and fulfilling ESG mandates immediately.
C. Long-Term Value and Resale
Electric boilers have a significantly longer operational life than combustion boilers, often exceeding 30 years with proper maintenance, ensuring a strong long-term asset value.
5. Overcoming the Key Challenge: Electrical Load
The main challenge for transitioning to electric steam is ensuring the plant’s electrical infrastructure can support the large kilowatt demand.
- Assessment: A thorough electrical load audit is necessary to determine if existing transformers and switchgear can handle the load of a large ELECTROMAX unit.
- Staging Load: Most large electric boilers employ staged heating elements. They do not draw full power continuously; the load is spread out and modulated based on steam demand, preventing sudden massive power draws.
- Phased Implementation: Many plants begin by replacing small utility boilers with ELECTRON units or their hot water systems with ELECTRO AQUA units to test the technology and infrastructure before committing to a full-scale ELECTROMAX switch.
Conclusion: The Era of Clean Steam is Here
The ultimate guide to industrial steam generation in the 21st century points unequivocally toward electrification. The Electric Boiler is not just an equipment upgrade; it is a fundamental shift toward an operational philosophy defined by cleanliness, safety, and efficiency.
Whether your priority is IBR compliance with ELECTROMAX, compact, instantaneous steam with ELECTRON, or pioneering scale-free heating with INDUCTRON, IndianBoilers.com provides the highest quality electric solutions, ensuring your plant remains competitive, compliant, and sustainable in the low-carbon future.
Ready to calculate your potential savings and step into the era of clean steam?
Contact IndianBoilers.com today for an electric load assessment and a detailed ROI analysis for your specific industrial heating needs.