-
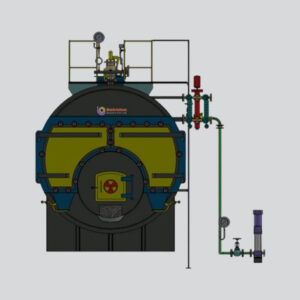
Industrial Boiler
High Pressure Industrial Steam Boiler 750 Kg/hr – Heavy Duty Boiler
₹1,380,000.00 Add to cart
Steam Boiler: Powering Our World
A steam boiler is a fascinating machine that makes modern life possible, from the electricity we use to the factories that make our goods. Essentially, it’s a giant, specialized teapot built to handle immense power.
What Does a Steam Boiler Do?
Simply put, a steam boiler’s job is to turn water into high-pressure steam.
- Heat is Applied: Fuel (like natural gas, oil, or coal) is burned in a furnace.
- Water Gets Hot: This intense heat is transferred to water contained within a strong, closed vessel.
- Steam is Created: When water reaches its boiling point, it turns into steam (a vapor). Because the vessel is sealed, this steam is trapped and the pressure builds up tremendously.
- Work is Done: This high-pressure steam is piped out to do work, much like compressed air.
Why is Steam So Powerful?
When water turns into steam, it expands its volume by about 1,600 times! This massive expansion is the source of the boiler’s power. That high-pressure steam can be used to:
- Generate Electricity: It blasts against the blades of a turbine, spinning it like a pinwheel. This spinning motion drives a generator to create electricity for your home.
- Run Factories: It heats chemicals, sterilizes equipment, or drives heavy machinery in manufacturing plants (like making textiles, paper, or processed foods).
- Heat Buildings: It can be circulated through radiators to keep large buildings or industrial facilities warm.
The Two Main Boiler Types
Boilers are generally categorized by how the heat meets the water:
| Boiler Type | Analogy | How it Works | Best For |
| Fire-Tube | Heating water in a pot with a coil | Hot combustion gases pass through tubes, and water surrounds the outside. | Smaller systems, lower pressure, quick response. |
| Water-Tube | Heating a hose over a fire | Water passes through tubes, and the hot gases flow around the outside. | Power plants, very high pressure, and large capacity. |
Keeping it Safe and Efficient
Because boilers operate under such high pressure, safety is the top priority. They include critical devices like safety valves, which automatically release steam if the pressure gets too high, preventing a catastrophic failure.
Modern boilers are also designed for high efficiency. They often use devices like economizers that capture and reuse the waste heat in the exhaust gases to pre-heat the incoming water, which saves fuel and money.
The steam boiler might seem like old technology, but it remains the engine room of global industry and power generation!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Fire-Tube and Water-Tube boilers?
- Fire-Tube (Smoke Tube): Hot combustion gases pass inside the tubes, which are surrounded by water. They are ideal for low-to-medium pressure applications (up to 20 TPH).
- Water-Tube: Water flows inside the tubes while hot gases circulate around them. These are used for high-pressure, high-capacity needs, such as power plants.
What does "Three-Pass" design mean?
It refers to the number of times the hot flue gases travel the length of the boiler before exiting the chimney. A three-pass design maximizes heat transfer, significantly increasing the boiler’s thermal efficiency.
What is a "Packaged" Boiler?
A packaged boiler comes as a complete, factory-assembled unit including the burner, pump, and controls. At indianboilers.com, our packaged units are "Plug & Play," meaning they require minimal onsite assembly and can be commissioned rapidly.
How do I determine the right boiler capacity for my plant?
Capacity is measured in kg/hr or TPH (Tons Per Hour). You should calculate your peak steam demand by adding up the requirements of all your machines and adding a 10-15% safety margin for future expansion or heat loss.
What is the typical lifespan of an industrial boiler?
With high-quality manufacturing and consistent maintenance, a boiler from indianboilers.com typically lasts 20 to 25 years.
How can I improve the efficiency of my existing boiler?
Efficiency can be boosted by:
- Installing an Economizer to pre-heat feedwater using waste flue gas.
- Installing an Air Pre-heater (APH).
- Ensuring regular "soot blowing" to keep tubes clean.
- Using a high-quality water softener to prevent scale.
What is the difference between IBR and Non-IBR boilers?
- IBR (Indian Boiler Regulations): Mandatory for boilers with a capacity over 25 liters or high pressures. They must be inspected and certified by government authorities.
- Non-IBR: Used for very small capacities (often called Small Industrial Boilers or SIB) where strict government registration isn't required, though safety standards still apply.
What are "Boiler Mountings" and "Accessories"?
- Mountings: Essential safety items like Safety Valves, Water Level Indicators, and Fusible Plugs.
- Accessories: Items that increase efficiency but aren't mandatory for operation, like Economizers or Superheaters.
Why is water treatment so critical?
Hard water creates "scale" (calcium buildup) inside the boiler. Just 1mm of scale can increase your fuel consumption by 7–10% and eventually lead to tube failure or even a boiler explosion.
How often does a boiler need a blowdown?
A "Blowdown" removes concentrated solids and sludge from the bottom of the boiler. Depending on your water quality, this should usually be done at least once per shift (every 8 hours).
What safety features are included in your boilers?
Our boilers feature redundant safety systems, including high-pressure cut-offs, low-water level alarms, flame sensors (for oil/gas), and spring-loaded safety valves.
What is the price of a 1 TPH Industrial Steam Boiler in India?
As of 2025, a standard 1 TPH (1000 kg/hr) IBR-certified boiler typically ranges from ₹8 Lakhs to ₹15 Lakhs, depending on the fuel type and degree of automation.
Which fuel is the most cost-effective?
- Biomass (Husk/Briquettes): Lowest running cost but requires more labor/ash handling.
- Natural Gas: Cleanest and very efficient, but requires a pipeline.
- Oil (Diesel/FO): High running cost but very low maintenance and compact.
What factors influence the final price of a boiler?
The cost is determined by:
- Steam Capacity (TPH)
- Working Pressure (kg/cm²)
- Fuel Type (Solid vs. Liquid/Gas)
- Automation level (Manual vs. PLC-based)
- Material grade (Standard vs. Stainless Steel for clean steam)
What is the typical ROI (Return on Investment)?
Most of our clients see an ROI within 12 to 18 months, primarily driven by the fuel savings achieved through our high-efficiency designs compared to older or poorly maintained units.
Which industries use your steam boilers?
Our boilers are currently serving:
- Textiles (Dyeing & Finishing)
- Food & Beverage (Pasteurization & Cooking)
- Pharmaceuticals (Sterilization)
- Rice Mills (Parboiling)
- Chemical Processing
Do you provide installation and commissioning?
Yes. indianboilers.com provides end-to-end support, from site layout and chimney design to installation, piping, and final commissioning with IBR approval.
What kind of after-sales support do you offer?
We offer Annual Maintenance Contracts (AMC), 24/7 technical assistance, and a ready stock of genuine spare parts to ensure your production never stops.
How do I get a custom quote for my facility?
Visit our Contact Us page at indianboilers.com or message us directly on WhatsApp with your steam requirement and preferred fuel. Our engineers will provide a detailed technical and commercial proposal within 24 hours.